

Adverbs are words that modify other verbs, adjectives, other adverbs, or even whole sentences. They usually end with a “ly,” but not always.
Let’s discuss a few examples to understand the concept of adverbs better.
However, adverbs are not as simple as shown in the examples above. Adverbs not only tell what a verb does, they can also describe things like when, how, where, frequency, and intensity of the verb.
To make its use more accessible, let’s discuss the different kinds of adverbs. They will further clarify your concepts and ease the usage of adverbs in your writing.
The table below will help you understand and differentiate the different types of adverbs:
| Sr. No. | Name of Different Types of Adverbs | Definition | Examples |
| 1. | Adverbs of Manner | Adverbs of manner tell us how something happened or occurred. |
|
| 2. | Adverbs of Time | Adverbs of time tell us when something happened. |
|
| 3. | Adverbs of Place | Adverbs of place tell us where something happened. |
|
| 4. | Adverbs of Degree | Adverbs of degree tell us to what extent/degree something happened. |
|
| 5. | Adverbs of Frequency | Adverbs of frequency tell us how often something occurred. |
|
| 6. | Adverbs of Confirmation & Negation | Adverbs that confirm or negate an action. |
|
| 7. | Adverbs of Conjunction | Adverbs of conjunction combine two clauses or ideas. |
|
| 8. | Adverbs of Comment | Adverbs that are used to make a comment on the entire clause or sentence. |
|
The placement of adverbs is a bit tricky. Adverbs can be placed at the beginning, middle, and end of a sentence.
For example:
Tomorrow, I will be leaving for work a bit earlier.
You have no idea how poorly he behaved with me.
This answered all my questions clearly.
The table below will help you figure out how to place or use adverbs in a sentence correctly.
| Sr. No. | Placement | Types of Adverbs | Examples |
| 1. | At the beginning of the sentence | “Adverbs of conjunction” “Adverbs of Time” | Conjunction: I was not feeling well. However, I didn’t skip work. Time: Sometimes it is okay to be sad and take some time to yourself. |
| 2. | In the middle of the sentence. | “Adverbs of Comment” “Adverbs of Frequency” “Adverbs of Confirmation” | Comment: He behaved mischievously by hiding this from me; I should have known all the facts. Frequency: I can sometimes act very harshly. Confirmation: He would certainly be back by then. |
| 3. | At the end of the sentence | “Adverb of Manner” “Adverb of Time” “Adverb of Place” | Manner: He finished his homework speedily. Time: He is on time daily. Place: I was watching a movie there. |
A group of two or more words, without subject and verb, that further modifies a verb, adverb, or adjective is called an adverbial phrase.
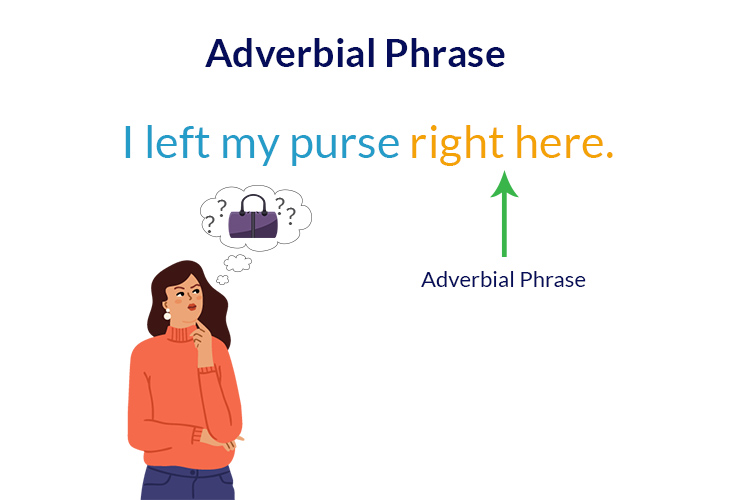
For Example:
A group of words with a subject and a verb, further modifying the meaning of a verb, adverb, or adjective, is called an adverbial clause.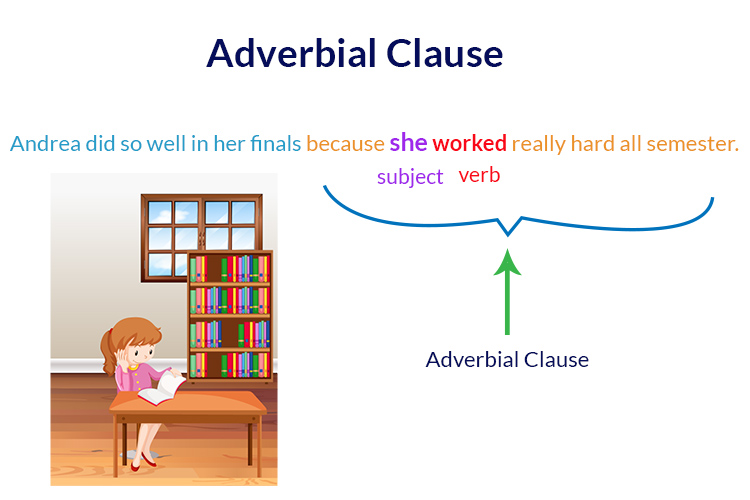
For Example:
Andrea did so well in her finals because she worked really hard all semester.
A phrase consisting of infinitive and verb(s) that modify the meaning of a verb, adverb, or adjective, is called an infinitive phrase.
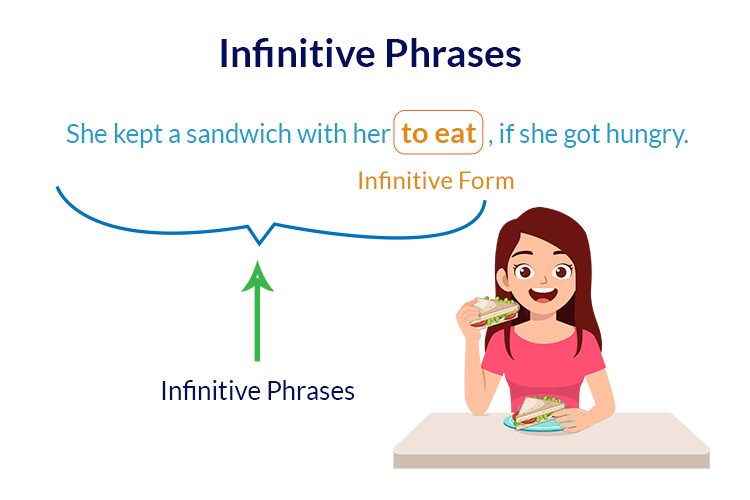
For Example:
She kept a sandwich with her to eat, if she got hungry.
A group of words that contain a preposition and a noun/noun phrase that take the place of an adverb of time or place to modify the meaning of a verb is known as a prepositional phrase.
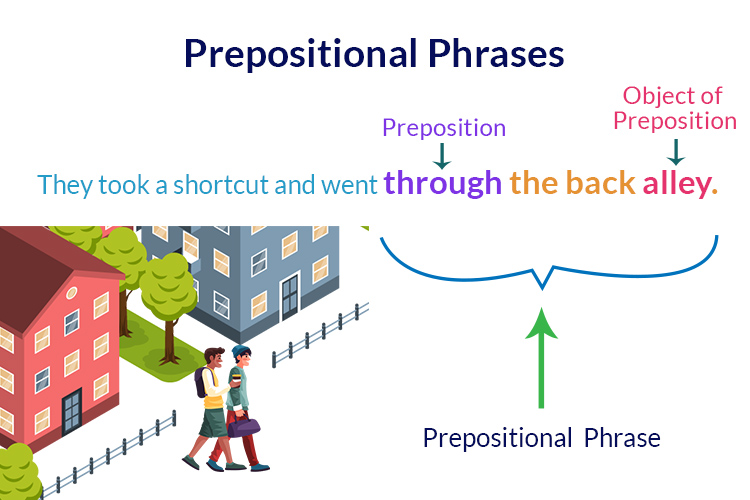
For Example:
They took a shortcut and went through the back alley.
Adverbs are a tautology, which means it is unnecessary repetition. It is used only because of poorly chosen verbs. It is often regarded as clutter in writing. The ly adverbs are usually weak verbs and should be avoided as much as possible.
Adverbs can easily be replaced or omitted, and your sentence would mean the same. It is sometimes considered a way of spoon-feeding the readers. But they don’t leave a good impression.
For Example:
She was extremely angry at her husband.
It can be written in a better way, like:
She was infuriated at her husband.
When you use very and extremely, it comes off as a sign of limited vocabulary on the writer’s part. So avoid very and extremely as much as you can, as it doesn’t leave a positive impression on the reader.
For Example:
She was extremely unhappy with the situation.
The sentence above gets better when you write it as:
She was disappointed with the situation.
Travelling is good for the spirit but very bad for the pocket.
Even when we remove very, the meaning of the sentence stills remains the same:
Travelling is good for the spirit, but bad for the pocket.
Always remember not to hyphenate the adverb when used to modify an adjective.
For Example:
This is a professionally-written piece of writing. (This doesn’t seem right)
This is a professionally written piece of writing. (This is Correct)
Except when the adverb can be used feasibly as an adjective.
For Example:
This article is well-written.
The media industry is a fast-growing profession.
Make sure you place your adverb appropriately so that the reader can quickly identify what the adverb is modifying in the sentence. Always try to put your adverb right next to the verb.
For Example:
The plaster fixed his broken arm quickly.
The above sentence is not clear, but when we write it like how it’s written below, it makes more sense:
The plaster quickly fixed his broken arm.
Above is an example of a squinting modifier, and then we have misplaced modifiers;
For Example:
Anna said after jogging, she would take a shower.
This sentence would make way more sense if moved after jogging to the end of the sentence:
Anna said she would take a shower after jogging.
However, limiting modifiers have significance and should not be avoided.
For example:
I only went home because I thought there were no more tasks.
Other limiting modifiers include; “hardly” and “nearly.”
Whenever you place an adverbial phrase or clause at the beginning of the sentence, always put a comma after it.
For example
Once upon a time, a beautiful princess lived in the tallest of towers outside the region.
Learning the English Language is not an easy task; as you can see, there are many ways to use adverbs. It is important to remember all the different types of adverbs, then there is the appropriate placement of the adverbs and different new concepts like adverbial phrases and clauses.
Just make sure you remember all the take-home points, detailing when to and when not to use adverbs, to avoid any grammatical errors pertaining to adverbs.
We hope this article helped understand the concept and usage of adverbs.
If you have difficulty learning the English language, get in touch with our qualified English Tutors; rest assured, you will never use incorrect Grammar again!