
Grammar mistakes are embarrassing but don’t worry, we all mess up sometimes. And it’s okay! English grammar can be confusing at times. However, we are here for your rescue and will help you overcome them.
The most commonly made grammar mistakes are due to homophones. Homophones are words that sound the same but differ altogether in meaning and usage. Use of then and than is one of the most common grammar errors made by people.
But who is to blame, the similar spellings, pronunciations, and even somewhat similar but entirely different usage, can be quite daunting.
Then is an adverb and is mostly used in time-related scenarios.
We use the word then in relation to time. At times it is used as an adverb, changing the meaning of other adverbs, and at other times it’s used as an adjective or a consequence.
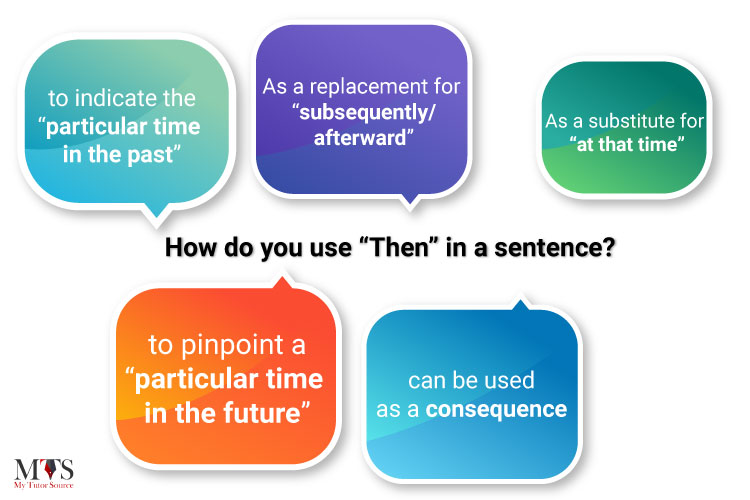
Let’s go through a few examples to see how and where “then” can be used:
1. As a substitute for “at that time”
Example:
You need to finish your homework first, then you can have your snack.
You need to finish your homework first, and at that time you can have your snack.
2. Then can be used as a replacement for “subsequently/afterward”, i.e. when we need to convey something that comes immediately after the other, in time or order.
Examples:
Go straight through the hallway, then take the first left.
Go straight through the hallway, afterwards/subsequently take the first left.
It was almost dawn break, then the sun shone bright and golden.
It was almost dawn break, afterwards/subsequently the sun shone bright and golden.
While baking a cake, first mix all your dry ingredients, then you can add your liquids.
While baking a cake, first mix all your dry ingredients, afterwards/subsequently you can add your liquids.
They had a long conversation, then they decided to go on their different paths.
3. Sometimes we use “then” to indicate the “particular time in the past”.
Examples:
Everything was so easy back then.
We were staying in a hotel then, before we got a permanent place in the city.
4. Also, then can be used to pinpoint a “particular time in the future”
Examples:
I will deliver the cake around 10 am, given that everything is prepared by then.
But by then, it will be too late to return.
5. Lastly, it can be used as a consequence.
Examples:
The traffic warden pulled me over for over-speeding, then he gave me a ticket.
Nobody woke me up so then I had to run to reach work on time.
Let’s discuss some commonly used phrases that consist of “then”:
Every now and then – it is mostly used when we want to say that something occurs sometimes, but not very often.
Example:
Every now and then I fall apart.
Yes, the lyric from the famous song “total eclipse of the heart”. Now you’ll never forget it.
And then some, it means something happened more than it was expected.

Then again, it is used as a substitute for “however”.
Example:
I would love to travel, but then again, who has the time.
Just then, it means suddenly.
Example: It was just then that I realized he never loved me.
Until then, it means until the concerned event occurs.

Than is a conjunction and is used while drawing a comparison between two things. It can also be used as a preposition at times.
Than is one of a kind word and it is often very hard to replace it with another word in the sentence. It is a conjunction used for comparison. It is often followed by words like few, lesser, younger, bigger, and so forth.

Here are a few examples:
I am younger than my sister.
He is even later than usual.
Fresh fruits are healthier than junk food
One exception to this rule is when we are not using “than” to make direct comparisons. As, we can find a replacement for it, as shown is the example below:
More than a hundred years ago, life was much simpler.
Can also be written as:
Over a hundred years ago, life was much simpler.
Or
You can’t apply for this job if you are younger than 18.
Could also be,
You can’t apply for this job if you are under 1.
You can remember a few common phrases using than, so you don’t misspell. Here are a few common examples:
Blood is thicker than water, which means blood relations are stronger as compared to the rest.
Better late than never, which means that showing up late is better than not showing up at all.
It’s better to give than receive, which is used to imply the importance of generosity.
The pen is mightier than the sword. It implies diplomatic dialogue has a bigger impact as compared to war.
Better you than me, an expression for thank God I’m not the one going through this, as you can deal with this situation better than I can.

Most people get confused with the “than me” or “than I” issue, as to some “than me” sounds more natural, and to others “than I”. But the truth is both are accurate and it depends on context. However, adding “am” after I, can make it more accurate.
For instance,
“He is taller than me”, “He is taller than I”, and “He is taller than I” are all correct. “Than I” is a more succinct version, whereas “than I am” is more comprehensive. But all three are acceptable forms.
You can easily differentiate between the two by remembering “then” is related to time, whereas “than” is used while making comparisons.
There’s also a mnemonic you can memorize to help you identify the difference between the two.
“Then” and “time”, both have the letter “e” in them and “than” and “comparison” both of the letter “a” in them. So use then when we are referring to time, and than for when we are making comparisons.
The use of then vs than is very confusing. However, we should still consider ourselves lucky, as people in the middle ages had it tougher than us. Yes!! For they had the same spelling for both back then, and it was a task for the readers to understand what it means based on text context.
But once you know the difference, the rules, and the exceptions, you will never be wrong again. Even if you do, you can recall the mnemonic and it will come back to you naturally.