
The human nervous system is a very fascinating organ controlling sensory and hormonal regulation and maintaining the homeostatic balance in the body.
Here you can read all about the basic functions of the human nervous system and a detailed review on the parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous systems. Do you wish to learn more comprehensive aspects of the human nervous system? Our private biology tutors provide detailed lectures as per your requirement.
Whether it is a voluntary action or involuntary action, they are all controlled by the nervous system. From your movement to your perception and thought process, all your major bodily functions are controlled by the nervous system.
A lot of our actions are controlled by our nervous system. All the components of our nervous system including the brain, spinal cord, somatic, and autonomic nervous system are actively working for the right body functions.
Let’s discuss some of the ways our actions are impacted by our nervous system which comprises the central nervous system and peripheral nervous system:
The human nervous system is classified into two main parts that include:
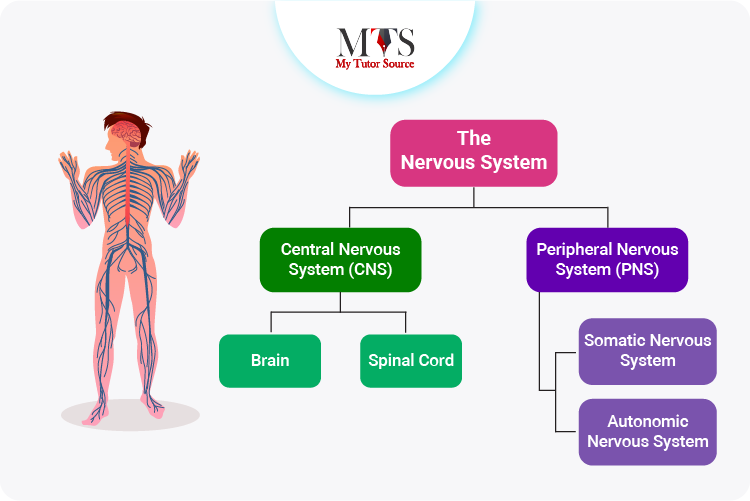
Just like we associate terms with their names, the functions of the autonomic nervous system are also associated with its name. The many autonomic functions in our body that we are usually not in control of, are controlled by the autonomic nervous system.
The autonomic nervous system is further classified into two main parts including
The sympathetic division is mainly associated with the flight or fight response of the body when the body’s response is usually associated with stress or pressure. Whenever there is a situation that is perceived as dangerous or stressful by us, the response to it is generated by the sympathetic nervous system.
The sympathetic nervous system is comprised of certain cell bodies that work to increase the blood flow to the muscles and accelerate the heart rate so basically whenever you are feeling a bit anxious, stressed, or experiencing a sudden panic attack, these all are responses by your sympathetic nervous system.
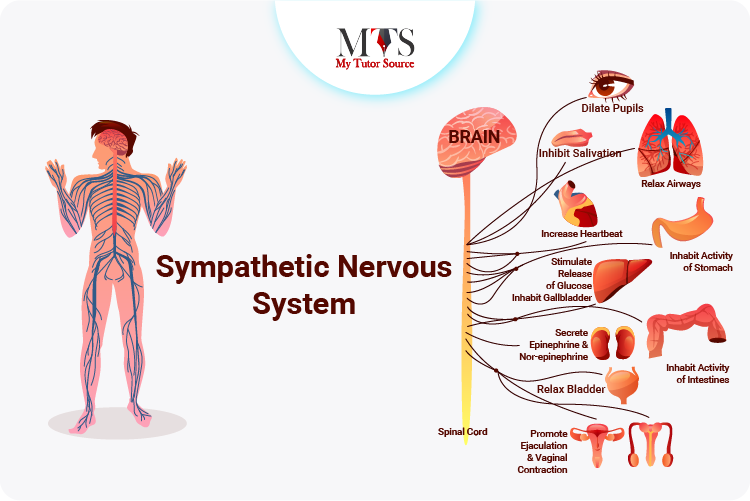
The sympathetic nervous system is located near the middle of the spinal cord. It starts from the first thoracic vertebra and goes forward till the second or their lumbar vertebra. It can be found near the thoracic and lumbar regions.
The sympathetic nervous system is responsible for preparing us for any dangerous or stressful situation that we might be encountering. This response by the sympathetic nervous system is achieved by a series of complex steps involving neurons, hormones, and other body organs including the skeletal system, gastrointestinal tract, and cardiac muscles.
After the sympathetic nervous system increases the release of stress hormones including adrenaline and noradrenaline, there are a series of changes in your bodily functions that you feel suddenly. These changes include
The impulse response is secreted by the sympathetic nervous system which in turn regulates the hormonal response. That response actively changes the physiological functions of the gastric, skeletal, and cardiac systems of the body. sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system.
As a result of a stressful situation, there is a sudden release of certain hormones that are associated with the stress factor in the body.
There is a bidirectional flow of messages associated with the sympathetic nervous system. As the sympathetic nervous system send the stress response to the body to release hormones, the release of certain hormones and their action on the other body organs are in return a response of the body to the sympathetic nervous system.
This is how there is a bidirectional flow of information going through the sympathetic nervous system to the body and then from the body to the sympathetic nervous system.
Several different functions are performed by the sympathetic nervous system to ensure that the body is functioning right as a result of a stressful or alarming situation, making it a quick response mobilizing system.
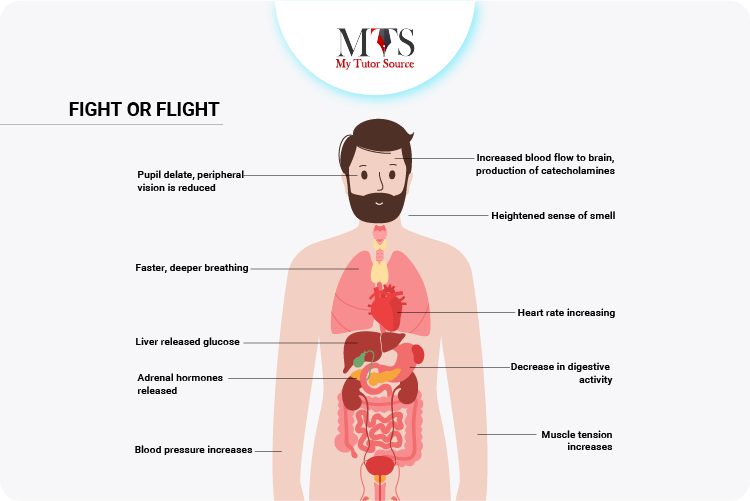
The sympathetic nervous prepares the body for any dangerous or stressful situation by the action of fight or flight response. With the action of fight or flight response, the body gets prepared to face a certain situation. Based on the decision, we either fight it or flee from it. This is how fight or flight response works that are generated by the sympathetic nervous system when we feel attacked or in a dangerous situation.
The male and female responses differ to certain situations. It has been noted that under stressful situations, males and females tend to act and behave differently from each other, Hence their actions during fight and flight response differs as well. For instance, if there is a certain stressful situation, the males would be less likely to open up to someone about it whereas females would prefer going to someone and talking it out.
Some researchers and evolutionary biologists believed that the sympathetic nervous system of people belonging from the very early times of evolution was quite active. Since there was a major goal of survival, and they had to stay alert and be prepared for the fight or flight response all the time, their sympathetic nervous system was almost all the time activated to ensure that their body is prepared for the survival response at any given time.
If we look at the early evolutionary times, when man was still learning about his surroundings, the fight or flight response was in a way that they either used to show aggression and confronted the threatening situation or they would run away from the situation that felt life-threatening to them such as identifying something a predator.
This is how the fight or flight response from the sympathetic nervous system helped the people from the early evolutionary times.
In the current times, the fight and flight response has been modified in action since now there is no basic goal of survival so there are other ways we express the action of fight or flight response. Sometimes we express it by talking loudly or getting in an argument whereas to express the flight response we sometimes go quiet or start an addictive habit that might keep us away from that stressful situation.
The sympathetic nervous system is responsible for regulating the body temperature hence maintaining a homeostasis balance in the body. Using the fat reserves in the body and through the rush in the blood flow, the sympathetic nervous system raises the body temperature as per requirement. When needed, it brings it down to a cooler level through the sweat glands.
Sometimes we experience our body getting heated up in an alarming situation whereas sometimes our hands and feet feel cold when we are encountered with a threatening situation.
This temperature regulation is done mainly by the sympathetic nervous system.
The sympathetic nervous system is responsible for increasing the heart rate when required by the body. In some situations like running or sitting down when you are standing, there is a need to increase the heart rate to avoid the situation of dizziness or faintness.
Whenever we encounter a threatening or alarming situation, we feel our heartbeat suddenly getting increased, this is done mainly by the release of certain hormones by the sympathetic nervous system. If there was no rush in the heart rate, we would suddenly faint at the encounter of any such alarming situation.
The parasympathetic division works as a counteraction to the sympathetic nervous system. When the sympathetic nervous prepares the body for a fight or flight response, the parasympathetic nervous system is responsible for maintaining the normal bodily functions and bringing the body to its normal and resting state once the body has encountered a certain alarming situation.
When the body’s functions like a heartbeat or body temperature increases by the sympathetic nervous system as a result of an alarming situation, the body conditions need to be brought back to normal. This is done mainly by the parasympathetic nervous system as it brings back the heartbeat, temperature, and other body functions to normal.
Basically, the parasympathetic nervous system is there to make sure that the body functions are continued as per normal like they usually function.
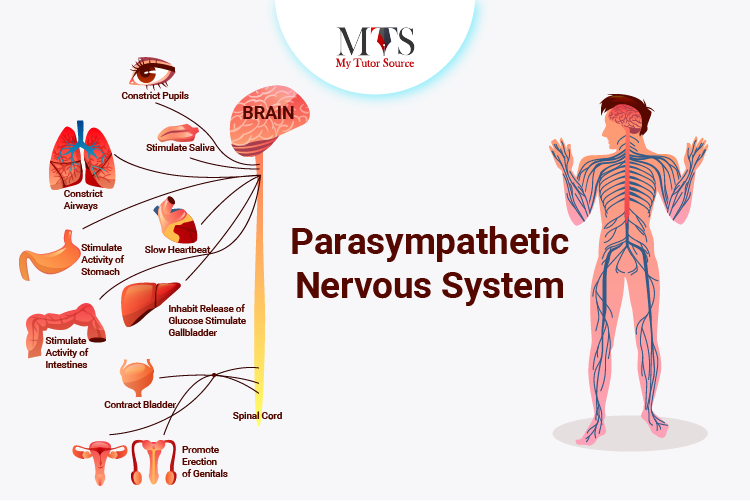
The parasympathetic nervous system is situated near the brain and through the long fibers, the parasympathetic nervous system extends to the particular organs where the resting state is required, mainly the lungs, bladder, stomach, and heart.
The nerves from the parasympathetic system arise from the sacral region of the spinal cord.
Here we have discussed the basic aspects of the parasympathetic nervous system that facilitates the normal working of the system
There are several ways through which the parasympathetic nervous system ensures that there is enough fluid release at required places to continue normal bodily functions.
When our eyes get dry due to a fight or flight response or any given situation, the parasympathetic nervous system makes the release of tears available so that the eyes are lubricated to avoid being dried out.
The parasympathetic nervous system ensures the normal secretion of salivary glands so that there are normal digestive operations after an upset gastric event.
It also contracts the bladder so that there is normal urination after an upsetting event.
Mainly the parasympathetic nervous system brings the body to its normal functioning by controlling the secretions of certain glands. Several changes are noticed in the body as a result of the action by the parasympathetic nervous system. These changes can include:
There are certain roles and functions that are associated with the parasympathetic nervous system as discussed below.
The main function of the parasympathetic nervous system is the exact opposite of fight or flight response and that is rest and digest. The parasympathetic nervous system is responsible for bringing the body back to its normal functioning where it is at a state that is more at rest and all the bold functions like digestion and heart rate have come back to normal.
In this way, the fight or flight response of the body is brought back to normal by the rest and digest mechanism by regulating the gland secretion.

In other words, we can say that the parasympathetic nervous system can also be referred to as the rest and digest response of the body because this is all the role that is performed by the PNS. After an emergency has passed, the body comes back to normal regulation by the parasympathetic nervous system.
To better understand the functions of the parasympathetic nervous system a popular acronym can be used here that is SLUDD.
This is a common acronym that completely covers the main roles and functions associated with the parasympathetic nervous system. SLUDD means:
Let’s further discuss the roles and functions of the parasympathetic nervous system based on this term.
After we have experienced a rather dry mouth as a result of an upsetting or alarming event, the parasympathetic nervous system acts on the salivary glands to secrete more than usual saliva to ensure that the mouth is lubricated enough for the normal eating and chewing functions of the body.
The parasympathetic nervous system achieves this by simply regulating the secretions of the salivary glands that are present in the mouth. These glands control the secretion of saliva in the mouth.
After a stressful or alarming event, the eyes are usually dried out. The parasympathetic nervous system ensures that there is enough flow of tears in the eyes by the process of lacrimation so that the eyes won’t dry themselves out.
If there are not enough tears in the eyes or if the eyes are not lubricated enough, the eyes being a sensitive organ would dry out eventually. To avoid this, the parasympathetic nervous system restores the normal functioning of the eyes through the proper release of tears in the eyes.
The pelvic nerve originating from the spinal cord region is actually responsible for the active flow of urination in the body after a fight or flight response. When the body is unable to urinate properly after a stressful event, the parasympathetic nervous system.
This is done by the contraction of the bladder. The parasympathetic nervous system sends signals via the pelvic nerve which in turn contracts the bladder leading to the normal flow of urination in the body.
There are several ways through which the parasympathetic nervous system brings the digestive operations back to normal. Firstly it stimulates the release of saliva which helps in the smooth flow and breakdown of food in the mouth and the stomach.
The parasympathetic nervous system also stimulates the movement of the stomach muscles more commonly known as peristalsis. This helps the food moves faster and smoothly to the other organs for further digestion.
Other than these functions, the parasympathetic nervous system also controls the release of bile. Bile is responsible for the normal digestion of fats. Under stressful conditions, the body might refrain from the release of bile hence the parasympathetic nervous system ensures the normal release of bile for normal digestion of fats.
The parasympathetic nervous system ensures that the movement of food is right along the pathway of all organs so there would be normal bowel movement when required.
Any unsettling event can hinder the normal bowel movement, this is brought back to normal by the action of the parasympathetic nervous system on the targeted organs.
There are some certain cranial nerves are associated with the parasympathetic nervous system working to regulate the normal functioning of the system including:
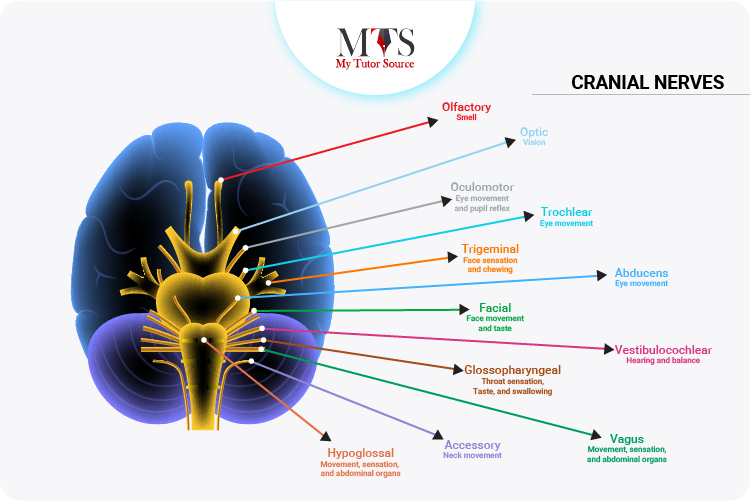
Although the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems are both parts of the autonomic nervous system and work on the automatic or involuntary actions of the body, there are differences in both systems that make their functions opposite to each other.
Let’s discuss some of the major differences between the parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous systems!
The sympathetic nervous system: The pupil is dilated and enlarges when there is any alarming or stressful event that requires the fight or flight response by the sympathetic nervous system.
The parasympathetic nervous system: in contrast, the pupil comes back to normal and it is constricted as it should be when the fight and flight response has passed and the body comes back to normal body function as a response of the parasympathetic nervous system.
The sympathetic nervous system: during a fight or flight response by the sympathetic nervous system, the heart rate is suddenly increased. We feel a sudden surge in the way the heart is beating making us breathe faster as well.
The parasympathetic nervous system: After the stressful situation has passed, the parasympathetic nervous system works to bring the heart rate back to normal. When the heart rate is decreased to a normal level, it also brings back the breathing to normal.
The sympathetic nervous system: the lungs during a fight and flight response by the sympathetic nervous system tend to dilate causing faster breathing.
The parasympathetic nervous system: On the other hand, the lungs usually come back to their normal resting state by the action of the parasympathetic nervous system. This is done by the constricting of the lungs which leads to normal breathing.
The sympathetic nervous system: when the body is encountered with a fight or flight response, the sympathetic nervous system increases the flow of blood to certain organs. In this way, we experience an increase in blood pressure when we encounter an unwanted or unsettling event.
The parasympathetic nervous system: After the passing of the fight or flight response, the parasympathetic nervous system comes into action to bring the blood flow to all body organs to normal. Hence restoring the normal blood pressure.
The sympathetic nervous system: as the body experiences any upsetting event, the gland secretions slow down and ultimately it hinders the activity of the digestive system.
The parasympathetic nervous system: After the fight or flight response is over, the parasympathetic nervous system ensures the normal gland secretion which in turn helps in bringing back the stomach activity and food movement to normal.
The sympathetic nervous system: The sympathetic nervous system is responsible for constricting the blood vessels, this restricts the blood flow activity, and increased pressure is required for the blood to flow hence increasing the blood pressure.
The parasympathetic nervous system: when the parasympathetic system comes into action, it dilates the blood vessels which helps to bring the blood pressure back to normal.
The sympathetic nervous system: The sympathetic nervous relaxes the urinary bladder and as a result of this, the body’s ability to pass the urine as per normal is hindered.
The parasympathetic nervous system: when the body functions are to be brought back to normal, the parasympathetic nervous system constricts the urinary bladder and eases the flow of urine from the body hence increasing the urine output.
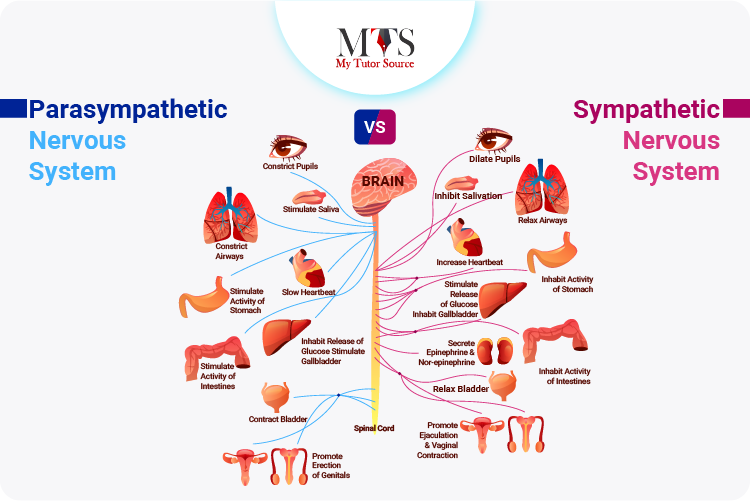
The autonomic nervous system is the part of the nervous system that regulates and controls the involuntary actions of the body. It is further divided into two parts, the Sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems. The sympathetic nervous system deals with the fight and flight response of the body and develops alertness in response whereas the parasympathetic nervous system brings the body back to its normal resting state as it should be.
The study of the human nervous system is a vast and fascinating area to explore. Learn about the in-depth aspects of the human nervous system by our professional home tutors.