

A mixture can be defined as substances that are composed of two or more than two forms of matter. You can separate a mixture by using physical methods. Moreover, in mixtures, the components that make up its structure do not undergo any sort of chemical changes. As a result, the individual properties of the components of a mixture remain intact and do not change. Some examples of mixtures would be salt and water, water and sugar, air, and different gases, etc.

In other words, we can say that a mixture is a thing you get as a result of combining two different substances so that no chemical reaction occurs between them and you can separate the substances if you want. Even when in the form of a mixture, the substances that make up the components of a mixture keep their own chemical identities separately. Normally, mechanical mixing is used to combine different components of a mixture, however, you may get mixtures by other procedures as well such as osmosis and diffusion.
Let us take a look at what are some mixtures in chemistry. There are two types of mixtures that are referred to in chemistry:
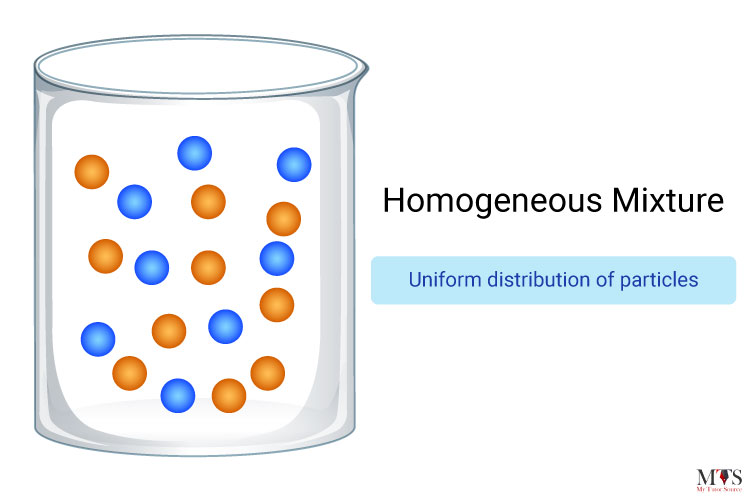
Homogeneous mixtures can be defined as mixtures that possess a uniform composition through all their substances. For example, sugar and water, salt and water, soft drink water, lemonade, and air are all examples of homogeneous mixtures. One of the most classic examples is, of course, salt and water, on the grounds that the limit between water and salt can never be separated. When a mixture reaches that point you cannot see the path of light if you pass a beam of light through that mixture.
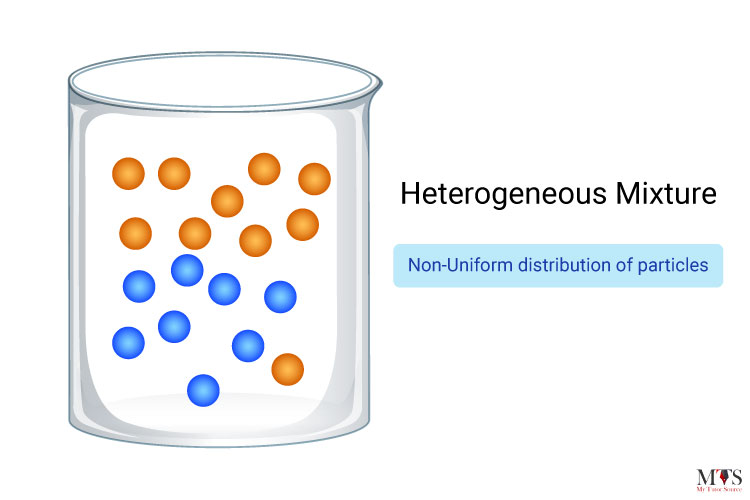
Heterogeneous mixtures can be defined as mixtures that do not possess a uniform composition through all their substances. For example sulfur and iron filings, soil and sand, oil and water, and so on because none of them have a uniform composition. This assumption is, however, made on the grounds that such mixtures have two more than two distinct phases.
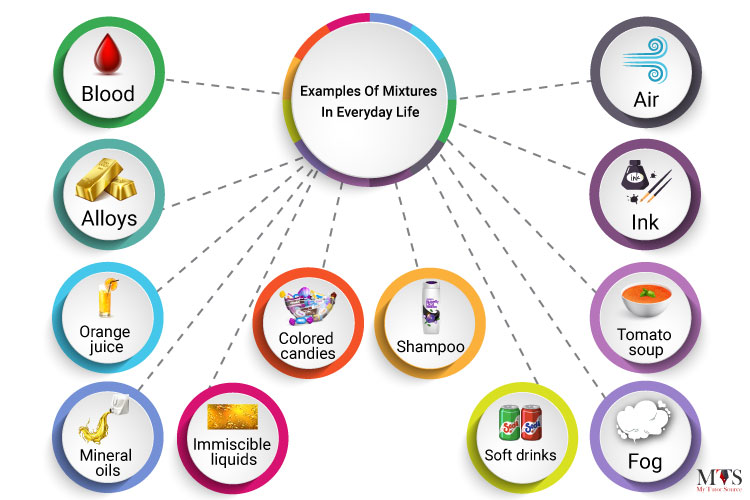
Here are some of the best examples of mixtures in everyday life:
Mixtures are everywhere around us, all we need to know is how to identify and differentiate them.